下一个更大元素
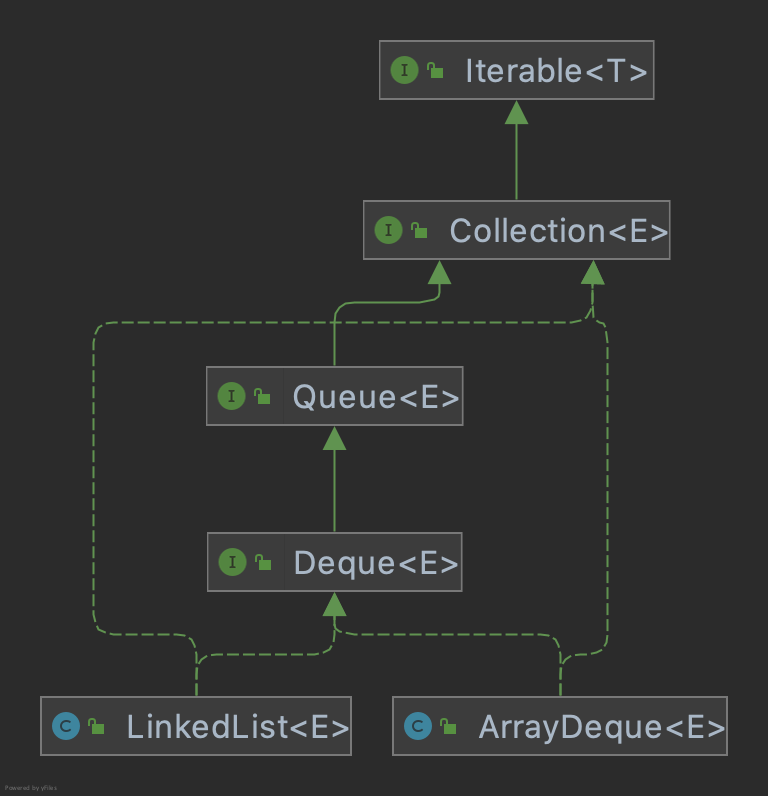
单调栈的一个应用是求下一个更大的元素。其中用到的较多的是接口Deque,类图结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
// 单调栈 + 哈希表
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 方便返回答案
// Deque 是双端队列
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 逆序遍历数组
for (int i = nums2.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 如果栈不为空,并且当前的值比栈顶元素大,则抛出栈顶元素,因为不可能是下一个更大元素
// 直到栈为空或者找到下一个更大的元素
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums2[i] >= stack.peek()) {
stack.pop();
}
// 存储当前数的下一个最大元素,数组中没有重复元素,因此可以使用HashMap
map.put(nums2[i], stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek());
// 向栈中添加当前元素
stack.push(nums2[i]);
}
int[] ans = new int[nums1.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
ans[i] = map.get(nums1[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
|
这里要求的是循环数组,可以转换为上一题,也就是一个长度为 2 * n 的数组用上一题的方法,实际上可以通过指标取模来达到这个效果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
// 单调栈 + 循环数组
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
// 用指标取模来模拟有 2 * n 长度的数组[0, ... , n - 1, 0, ... , n - 1]
for (int i = 2 * n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i % n] >= stack.peek()) {
stack.pop();
}
res[i % n] = (stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek());
stack.push(nums[i % n]);
}
return res;
}
}
|
这道题依然是下一个更大元素的变形,换汤不换药,栈中存放的是数组的下标。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
// 单调栈
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int[] ans = new int[temperatures.length];
// 为了返回天数,栈中存放的是数组的下标
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = temperatures.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] >= temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
stack.pop();
}
ans[i] = stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : (stack.peek() - i);
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
|
思路是:利用单调栈,栈中的元素按高度递减,如果栈中至少有两个元素,说明高度在下降,而如果当前元素的高度比较高,那么就可以形成一个洼地,能够接雨水。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
// 单调栈
public int trap(int[] height) {
int ans = 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int n = height.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) {
int top = stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
// 如果栈中存在至少两个元素,当前的值比较高,那么可以形成一个洼地,可以接雨水
int left = stack.peek();
int currWidth = i - left - 1;
int currHeight = Math.min(height[left] - height[top], height[i] - height[top]);
ans += currWidth * currHeight;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
|

